If you have a criminal record, there are so many ways it can affect your life.
For example, if potential romantic partners do a search for your name online, they might see something about it. If you want to get a new job, employers can see it as part of a background investigation. You might still be paying legal fees and fines related to it.
It’s difficult, but by knowing what you’re up against, you’re in a better position to move forward if you have a criminal record.
With that in mind, the following is a guide to having a misdemeanor and some of the particular implications it can have for you in your life or the life of your loved one.
The Basics
A misdemeanor is a less serious crime than a felony. Felonies are the most severe crimes that someone can commit. A felony often involves prison or jail time, fines, and perhaps permanent loss of certain freedoms.
With a misdemeanor, you might still have jail time, but it’s shorter, and fines may be smaller. You might also face temporary punishments rather than permanent losses.
There’s another category of offense that most state criminal systems use in the U.S., which is an infraction. An infraction is the least serious type of crime. An infraction means you broke a rule, law, or ordinance, and typically there’s no jail time. An infraction doesn’t usually appear on a criminal record either, and the only punishment is a fine.
A traffic ticket is an infraction, as are petty offenses like littering or disturbing the peace.
What is a Misdemeanor?
A misdemeanor, as mentioned, is more serious than an infraction. In most states, this type of criminal offense can have a possible jail term of up to a year.
There are three classes of misdemeanors under federal sentencing guidelines.
A class A misdemeanor carries possible jail time of a year or less but more than six months. Class B misdemeanors have potential jail time of six months or less but more than thirty days. A class C misdemeanor is thirty days or less, but more than five days.
A gross misdemeanor is an offense that’s more serious. These usually contribute to more severe penalties. The definition of what would constitute a gross misdemeanor is defined by state law.
For misdemeanors, usually, any jail time is served in local county jail and not a high-security prison. There’s a lot of flexibility for prosecutors as far as the crimes they charge, the punishment, and the plea bargains they’ll negotiate.
What is a Felony?
For comparison, a felony is the most serious crime classification. The federal government describes felonies as crimes with a punishment of more than a year, but states aren’t as strict about individual definitions. For example, in Maine and New Jersey, there’s no classification of criminal offenses. Some states will have the term felony, but it’s not formally defined.
In most states, the term is used and defined based on the length of a sentence or the place someone is incarcerated. Sometimes, it’s both.
Felonies are crimes like kidnapping, murder, and rape.
Misdemeanor Examples
A misdemeanor might be a crime like the following:
-
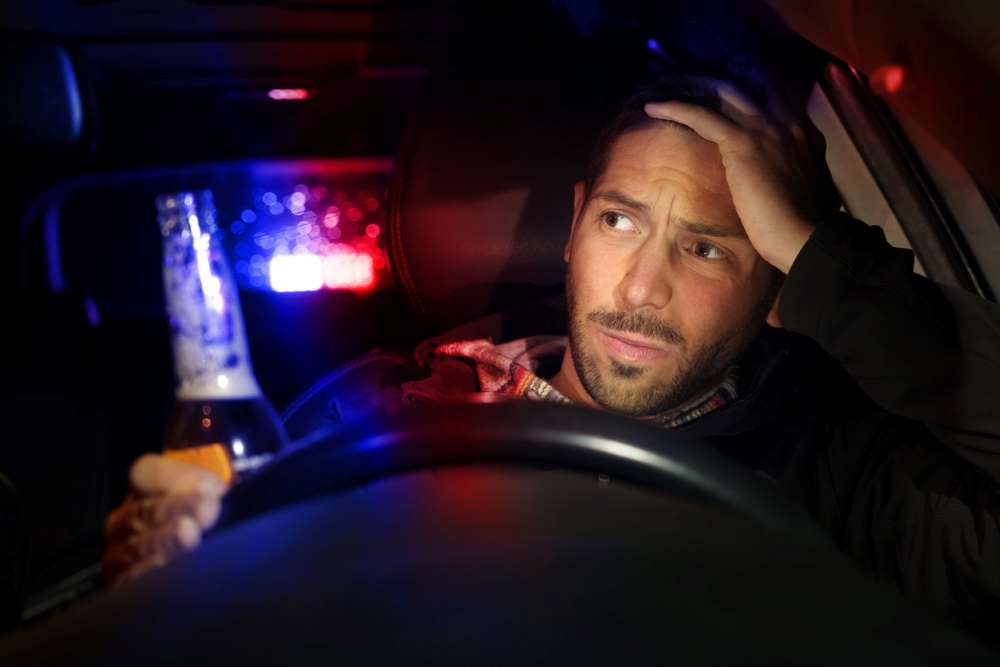
Traffic offenses involving being under the influence
-
Assault and battery or other charges that involve bodily harm
-
Theft or larceny
-
Possession of controlled substances or drug crimes
-
Perjury
-
Gun possession violations
Punishments
As has been briefly talked about above, the criminal punishment for a misdemeanor can include jail time and criminal fines. Jail sentences usually are no more than a year, and fines are often capped at $1,000, but it depends on the state.
The consequences depend a lot on the type of violation.
The Impacts of a Misdemeanor On Your Life
Often, since a misdemeanor is less serious than a felony, people charged think it’s not a big deal. The reality is that it can have a serious impact on the rest of your life, so you should take every possible legal step to avoid a conviction.
Any type of criminal record can have impacts, including:
-
Employment: Any charge on your criminal record, even if you aren’t convicted, can impact your ability to find a job or advance in your career field. In the majority of cases, a prospective employer has the legal right to investigate your background, including your criminal record. They may also be legally able to avoid hiring you because of what they find. An employer might directly ask you if you’ve ever been charged with a crime. You have to answer truthfully, but you don’t have to disclose an arrest that didn’t lead to a conviction or a misdemeanor that was eventually removed from your record.
-
Child custody: If you have a criminal record and you share child custody, or you’re attempting to, there may be effects. If the charge involves violence, it can be especially impactful. A misdemeanor can cause you to lose your custody rights, particularly if the crime involves a family member. Similarly, if you ever wanted to adopt a child, a criminal record could prevent you from doing so.
-
Driving and privileges: If you have a criminal record, you can lose your license.
-
Gun ownership: Certain criminal convictions may cause you to lose the right to own a firearm.
-
College admission: For a young person, a crime, including a misdemeanor, can lead a college or graduate school to not admit you.
-
Professional licensing: If you work in a field like nursing requiring licensing, you may not be able to obtain the credentials needed if you have a misdemeanor on your record.
-
Renting a home: A landlord might be able to refuse to rent to you, depending on your criminal record.
There are things you can do to have your records sealed or expunged, and it can be worthwhile to look into if you have a misdemeanor on your record. Otherwise, the effects can be far-reaching and impact nearly every part of your life.