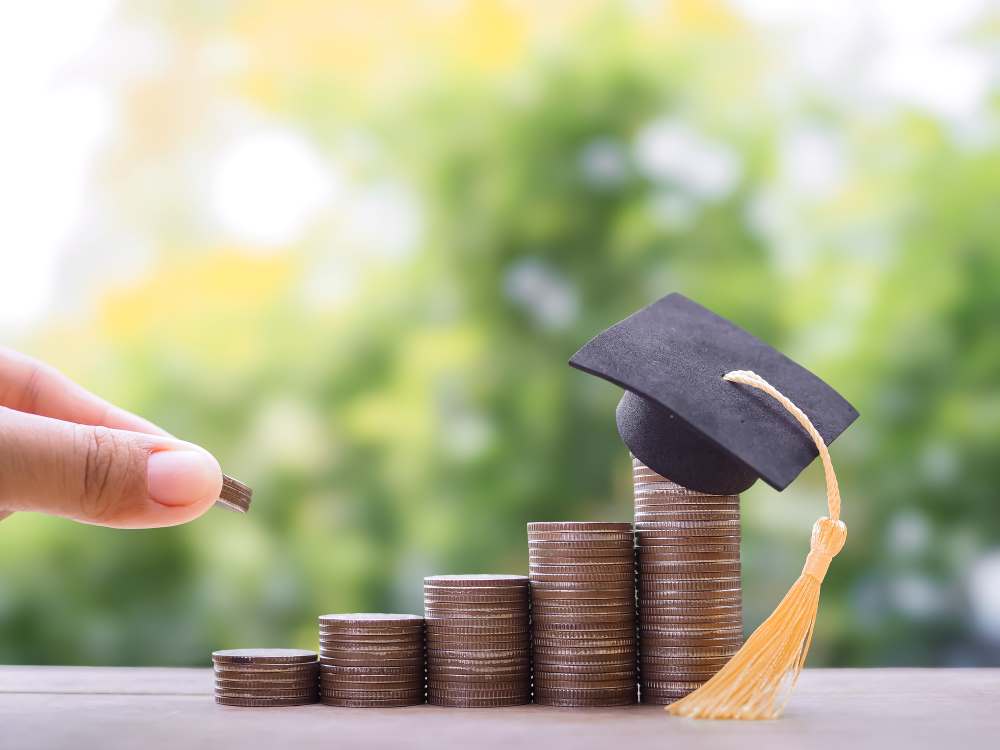
The cost of higher education has surged over the past several decades, making it harder for students and families to afford college without accumulating substantial debt.
While some inflation in tuition costs is expected, the steep and continuous increase has led to widespread concerns about the long-term financial burden on graduates. Many students now graduate with debt that takes years, or even decades, to repay.
Understanding why college tuition keeps rising requires a closer look at the factors driving these costs, including administrative expenses, government funding, and market demand. While the rising cost of education seems inevitable, students can take steps to manage their expenses and reduce financial strain.
From choosing cost-effective options to refinancing loans, some strategies can make higher education more affordable.
Managing Student Debt: Exploring Loan Repayment Options
For most students, borrowing is the only way to afford rising college costs. While loans make education possible, repayment can be a long and expensive process, especially with high interest rates. Many graduates find themselves making payments for years, struggling to balance debt with other financial goals.
One way to manage student loan repayment more effectively is through refinancing, which can lower interest rates and reduce monthly payments. To explore potential savings, borrowers can use Sofi’s refinance student loan calculator. This tool helps students compare their current loan terms with new options, making it easier to decide if refinancing is the right move. While refinancing isn’t for everyone, those with stable income and good credit may benefit from lower costs and faster repayment.
Administrative and Operational Costs
One of the biggest drivers of rising tuition costs is the increase in administrative expenses. Over the years, colleges and universities have expanded their administrative departments, hiring more staff for various services, including student affairs, diversity programs, and compliance management. While some of these positions contribute to improving the student experience, they also add to the overall operational costs of institutions.
Additionally, universities have invested heavily in modernizing campus facilities. From state-of-the-art dormitories to high-tech classrooms, these upgrades require significant funding. While such improvements enhance the quality of education and student life, they also contribute to rising tuition costs. Schools often justify these expenses by arguing that they attract more students, improve retention rates, and maintain institutional competitiveness. However, the financial burden ultimately falls on students and their families.
Declining State and Federal Funding
Historically, state and federal funding played a significant role in keeping tuition costs manageable. However, over the past several decades, many states have reduced their financial support for public universities. This has forced colleges to make up for lost funding by increasing tuition rates. The reduction in government assistance is often attributed to budget constraints and shifting political priorities.
With less public funding available, institutions have turned to alternative revenue sources, such as higher tuition fees and increased reliance on out-of-state and international students who pay higher rates.
The Impact of Market Demand
The demand for higher education has also contributed to rising tuition costs. Over the years, more students have pursued college degrees, leading to increased competition for enrollment. This has allowed institutions to raise tuition prices without experiencing a significant drop in applications.
Additionally, colleges have leveraged their reputation and ranking to justify tuition hikes. Many universities focus on improving their prestige by investing in research, faculty recruitment, and campus infrastructure. These efforts often come with higher operational costs, which are ultimately passed on to students in the form of increased tuition fees.
The Role of Private Institutions and For-Profit Colleges
Private universities and for-profit colleges have played a role in driving up overall tuition costs. Unlike public institutions that rely on government funding, private colleges set their tuition rates based on market demand and institutional goals. Many private schools offer generous financial aid packages, but their base tuition is often significantly higher than that of public universities.
For-profit colleges, in particular, have received criticism for their pricing structures. Some of these institutions charge high tuition rates while providing lower-quality education and limited job placement opportunities. Students who attend such schools often find themselves burdened with debt without the career advancement they expected.
What Students Can Do to Reduce Costs
While the rising cost of tuition is a complex issue, students can take proactive steps to minimize their expenses and reduce financial strain. One of the most effective strategies is to consider attending community college for the first two years before transferring to a four-year institution. This approach allows students to complete general education requirements at a significantly lower cost before moving on to a more expensive university.
Scholarships and grants are also valuable resources that students should actively pursue. Many organizations, private foundations, and institutions offer financial aid based on academic achievement, extracurricular activities, and financial need. Unlike loans, scholarships and grants do not need to be repaid, making them a crucial tool for reducing college expenses.
Another way to manage costs is by choosing in-state public universities, which often have lower tuition rates for residents. Additionally, some colleges offer work-study programs that allow students to earn money while gaining valuable work experience. This can help offset tuition costs and reduce reliance on student loans.
Budgeting and financial planning also play a crucial role in managing college expenses. Students should track their spending, prioritize essential expenses, and avoid unnecessary debt. Living at home, sharing housing with roommates, and cutting down on discretionary spending can all contribute to long-term savings.
The Future of College Tuition
Looking ahead, the cost of college is unlikely to decrease without significant policy changes. Some lawmakers have proposed measures to make higher education more affordable, including tuition-free community college programs and increased federal funding for public universities. However, the implementation of such initiatives remains uncertain.
All in all, the steady rise in college tuition has made higher education an expensive investment, but understanding the factors driving these costs can help students and families make better financial decisions. Administrative expenses, reduced government funding, market demand, and the influence of private institutions all contribute to tuition increases.