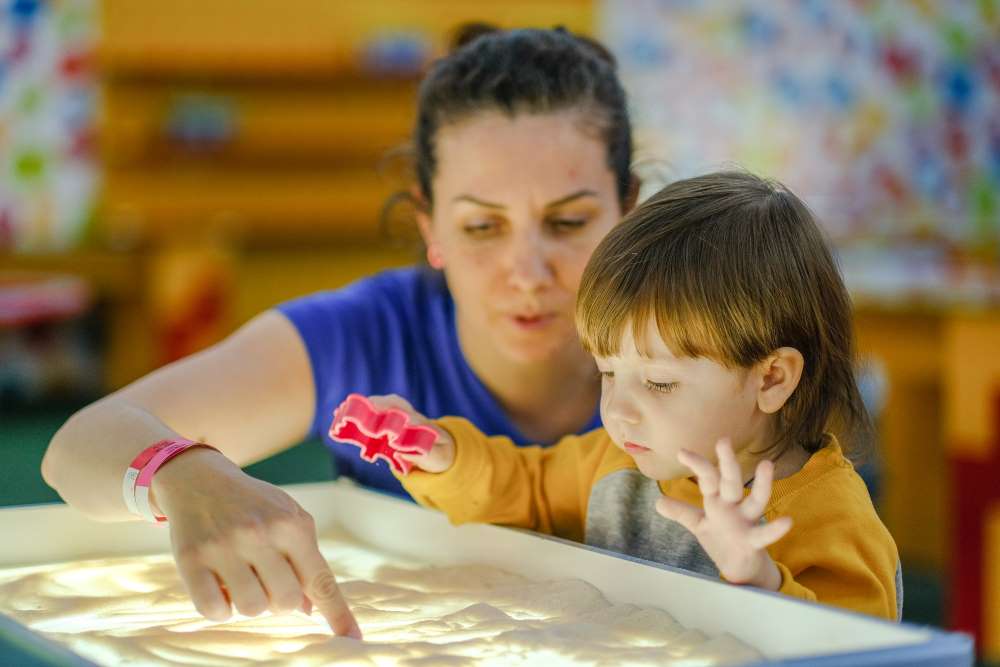
Autism spectrum disorder affects a person's behavior and interaction with the world around them. It's a life-long developmental disorder characterized by challenges with social communication, repetitive behaviors, and sensory processing difficulties. While autism can be diagnosed at any age, early identification in children is crucial for improving their quality of life through timely interventions.
This article discusses the common signs of autism in children and provides insights into what to look for. Continue reading for more.
Understanding Autism in Children
Autism spectrum disorder, or ASD, has characteristics that vary from person to person. Some children may exhibit mild symptoms, while others may face more significant challenges in daily life. The early signs of autism may be evident as early as 2 months of age, according to the Autism Science Foundation. However, a formal autism diagnosis may come later.
One of the most common signs of autism in children is difficulty with social communication. This can include limited eye contact, delayed speech, or challenges with nonverbal communication, such as gestures or facial expressions. They may also struggle to develop social skills, making it harder for them to form friendships or engage in typical childhood interactions.
Meanwhile, repetitive behaviors, such as hand-flapping, rocking, or self-stimulatory behavior, are another key indicator. These behaviors often serve as a way for autistic children to manage sensory input or cope with overwhelming emotions. Sensory processing issues are also prevalent, with some children experiencing intense reactions to sounds, textures, or lights, which can lead to sensory overload.
Signs of Autism in Infants and Toddlers
Parents and caregivers can look for specific indicators of ASD in babies and toddlers. For instance, a child with autism may not respond to their name by 12 months of age or show little interest in social games like peek-a-boo. Some children may also exhibit unusual play patterns, such as lining up toys instead of engaging in imaginative play.
The 'autism in babies checklist' often includes monitoring for delayed babbling, limited gestures (like pointing or waving), and a lack of shared enjoyment in interactions. By 24 months of age, if a child is not using two-word phrases or shows little interest in others, it may be worth discussing these signs with a healthcare provider.

Autism in Older Children
As children grow, the signs of autism can become more pronounced. Some may develop intense interests in specific topics, such as trains or rubber bands, and become intensely focused on these subjects. Others may struggle with changes in routine, exhibiting emotional reactions when their daily life is disrupted.
Communication difficulties often persist, with some children relying on echolalia (repeating words or phrases) or struggling to understand abstract language. Social skills may remain a challenge, making it harder for them to navigate group settings or interpret social cues.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
An early ASD diagnosis can significantly improve a child's quality of life. Interventions for autism, such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral interventions or training are most effective when started early. A child development specialist or health care provider can conduct an assessment for autism to determine if a child meets the criteria for a formal ASD diagnosis.
It's important to note that autism signs can vary from child to child. Some children may exhibit only a few autistic traits, while others may display a broader range of symptoms. High-functioning autism, for example, may involve milder symptoms that are harder to detect but still impact everyday life.
Autism in Girls and Women
Autistic women and girls are often underdiagnosed because their symptoms may present differently. They may be better at masking their challenges, such as mimicking social skills or hiding repetitive behaviors. Because of this, many get diagnosed later in life, sometimes not occurring until adulthood.
Supporting Children with Autism
If you suspect your child is at risk for autism, seeking an official diagnosis is the first step. A child development expert can guide you through the process, which may include autism assessments and consultations with a child development specialist. Early support can help children with autism spectrum disorder develop communication skills, manage sensory input, and improve their social interactions.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of autism in children is the first step toward providing them with the support they need. From repetitive behaviors to challenges with social communication, the indicators of autism spectrum disorder can vary widely. Early intervention and a proper diagnosis of autism can significantly contribute to a child's development and overall quality of life.
If you have concerns about your child's development, reach out to a healthcare provider. For more information, consider consulting a booklet for parents or a booklet adults with autism may find helpful. Understanding this lifelong condition is key to fostering empathy and inclusion.