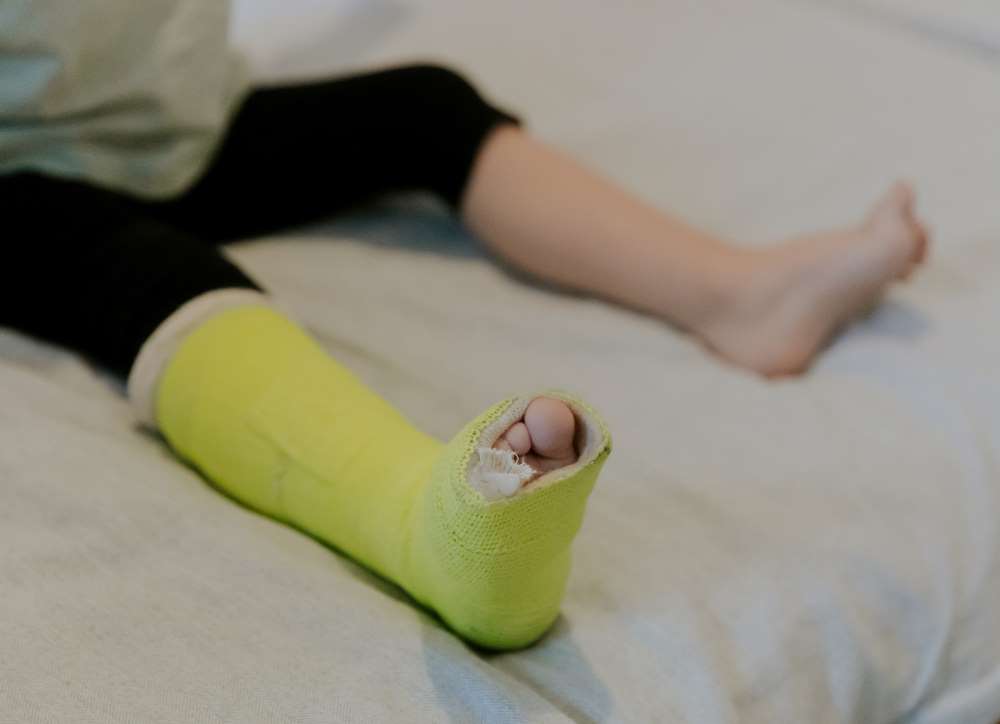
Children are naturally curious and often lack the foresight and experience to avoid dangerous situations. As a result, they are at a higher risk for injuries. Parents and guardians need to be aware of the common types of child injuries and know how to handle them if they occur. This blog outlines several prevalent child injury cases and provides guidance on dealing with them effectively.
Playground Injuries
Playground injuries are some of the most common accidents that children encounter. They can include falls, collisions, cuts, and fractures, often occurring when equipment is misused or poorly maintained.
Prevention Tips
-
Regularly Inspect Equipment: Check for sharp edges, rust, and weak structures.
-
Supervision: Always watch children closely as they play to intervene if necessary.
-
Age-Appropriate Design: Ensure the playground fits the child's age and development level.
Handling Playground Injuries
-
Address any severe injury immediately and seek professional medical attention if needed.
-
Notify the playground operator about any unsafe conditions that led to the injury.
Sports Injuries
Sports injuries range from minor scrapes and bruises to serious concussions and bone fractures. They can result from insufficient warm-up, accidental collisions, or aggressive play.
Preventive Measures
-
Appropriate Gear: Ensure children wear the correct protective equipment for their sport.
-
Proper Training: Educate on techniques to minimize injury risks.
Management of Sports Injuries
-
RICE Method: Use rest, ice, compression, and elevation for minor injuries.
-
For serious injuries, seek immediate professional help.
Burns and Scalds
Children can suffer from various burns, including thermal burns from hot objects, scalds from hot liquids, or even sunburns.
Prevention Strategies
-
Kitchen Safety: Keep children away from hot surfaces and liquids.
-
Sun Protection: Use appropriate sunscreen and limit sun exposure.
Treating Burns
-
Run cool (not cold) water over the burn for several minutes.
-
Gently cover the burn with a clean, dry cloth.
-
Severe burns require immediate attention from healthcare professionals.
Poisoning
Children may ingest household chemicals, medications, or plants, leading to poisoning. Symptoms can vary widely but may include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or breathing difficulties.
Poison Prevention
-
Secure Storage: Keep potential poisons locked up and out of reach.
-
Labeling: Clearly label all hazardous substances.
Responding to Poisoning
-
Try to determine what the child ingested.
-
Contact your local poison control center for immediate advice.
-
Adhere to any provided emergency instructions rigorously.
Choking and Suffocation
Small objects, foods, and even certain toys can pose choking risks to children, particularly those under the age of three.
Avoiding Choking Incidents
-
Childproofing: Keep small items out of reach.
-
Supervision with Food: Watch young children carefully while they eat, especially if they are still learning to chew properly.
Handling Choking
-
Stay composed to avoid alarming the child further.
-
Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts: Know how to perform these life-saving techniques.
-
If the child cannot breathe, call emergency services immediately.
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car accidents are a leading cause of injury for all age groups, and children are no exception. Proper restraint systems are crucial for preventing severe injuries.
Safety Measures for Motor Vehicle Accidents
-
Use age-appropriate car seats and booster seats.
-
Teach road safety and the importance of seat belts.
-
Never leave children unattended in or around vehicles.
If your car accident was caused by the negligent actions of another, then you need help from an experienced car accident lawyer to help your child recover. According to the car accident lawyers from Gray & White in Louisville, a lawyer will carefully calculate your damages to maximize the amount of compensation you recover. While monetary compensation for intangible damages like pain and suffering cannot undo the pain, it can help open doors to the best possible medical care and relieve financial burdens while you focus on your physical recovery.
Animal Bites and Attacks
Children are often naturally drawn to animals but may not recognize the signs of aggression, leading to bites or attacks.
Reducing the Risk of Animal Bites
-
Supervise any interactions between children and animals.
-
Educate your child on how to approach animals safely.
-
Ensure pets are vaccinated and properly trained.
Falls
Falls can happen anywhere, from the stairs at home to the school playground.
Fall Prevention
-
Safety Gates: Install gates at the top and bottom of stairways for young children.
-
Non-slip Mats: Use these in high-risk areas like the bathroom.
Dealing with Falls
-
Carefully assess the child for injuries without moving them hastily.
-
Offer comfort to the child to reduce anxiety.
-
If the fall seems severe or if there's any doubt about the child's well-being, consult a doctor.
While not all accidents can be prevented, understanding common child injury cases and how to handle them can significantly mitigate the risks and impacts of these injuries. Education, supervision, and preparation are key components in keeping children safe. For any injury, no matter how minor it may seem, when in doubt, always err on the side of caution and seek professional medical advice.