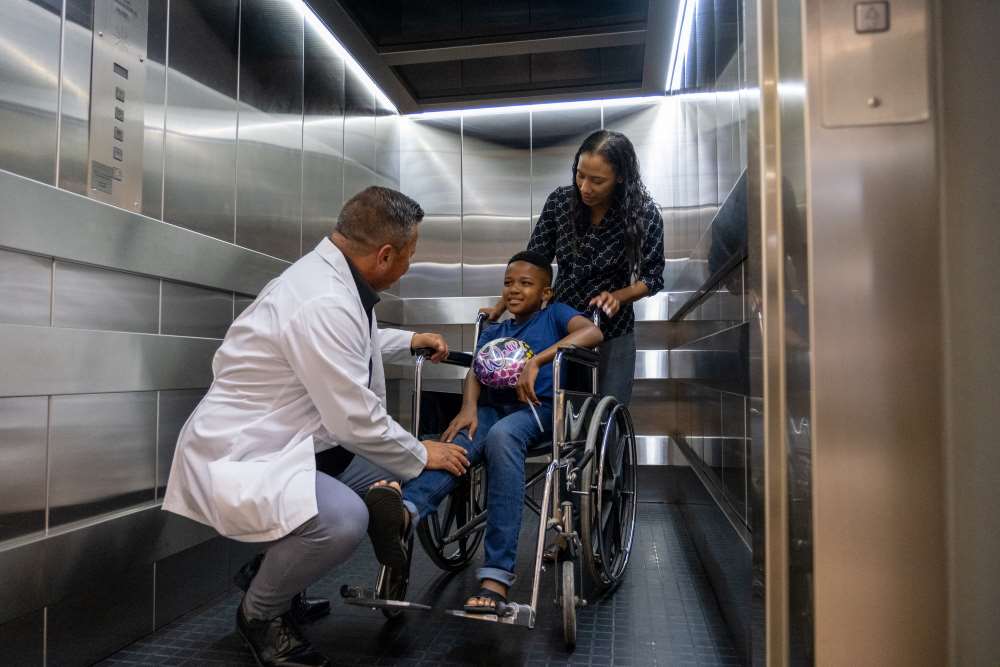
Childhood, a time filled with exploration, play, and learning, is also a period when children are particularly vulnerable to injuries.
Understanding the common causes of these injuries is crucial for parents, caregivers, and educators who strive to create safer environments for children.
By addressing these risks and implementing preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the incidence of child injuries and ensure a safer environment for their growth and development.
Falls
Falls are the leading cause of non-fatal injuries among children, encompassing a wide range of scenarios from toddlers learning to walk to older children engaging in more adventurous play like climbing trees or playground equipment. These incidents can result in various injuries, including bruises, fractures, and head trauma.
To prevent falls, supervision is key. Always keep a close eye on young children, particularly when they are on playground equipment or stairs. Use safety gates to block off staircases and ensure that playground equipment is suitable for the child’s age and is well-maintained. Additionally, at home, securing furniture to the wall and installing window guards can prevent falls from heights. In public spaces, make sure children are supervised and guided on how to safely navigate their environment.
Burns
Burns are another common cause of injury among children, resulting from various sources such as hot liquids, steam, fire, and electrical sources. Scalds from hot water and kitchen accidents are particularly common. Burns can be painful and may lead to long-term physical and psychological effects.
Preventing burns involves several practical steps. In the kitchen, keep hot liquids and foods out of reach of children. Use the back burners on the stove and turn pot handles inward to prevent children from grabbing them. Lower your water heater’s temperature to 120 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees Celsius) or lower to reduce the risk of scalding. Educate children about the dangers of fire and hot objects, and keep matches and lighters out of their reach. Additionally, installing smoke detectors throughout your home and regularly checking their batteries can provide an early warning in case of fire.
Drowning
Drowning is a leading cause of injury-related death in children, particularly those under the age of five. Children can drown in a surprisingly small amount of water, making bathtubs, pools, and even buckets potential hazards.
To prevent drowning, constant supervision is essential. Never leave children unattended near water, not even for a moment. In homes with pools, install a four-sided fence with self-closing and self-latching gates to keep children out when unsupervised. Swimming lessons can significantly reduce the risk of drowning; enroll children in age-appropriate swim classes and teach them water safety rules. Additionally, make sure to empty buckets, bathtubs, and other containers immediately after use.
Poisoning
Children’s natural curiosity often leads them to explore their environment by putting things in their mouths, making poisoning a significant risk. Common sources of poisoning include household cleaners, medications, and certain plants. Ingesting even small amounts of toxic substances can be dangerous or even fatal for children.
Preventing poisoning involves several strategies. Store medications, cleaning supplies, and other hazardous substances in locked cabinets and out of children’s reach. Use child-resistant packaging and keep products in their original containers to avoid confusion. Educate children about the dangers of unknown substances and the importance of asking an adult before eating or drinking anything. Additionally, be aware of common household plants that may be toxic if ingested and keep them out of reach or replace them with non-toxic alternatives.
Car Accidents
Car accidents are a major cause of injury and death among children, making the proper use of car seats, booster seats, and seat belts crucial. Children are especially vulnerable in car crashes due to their smaller size and developing bodies.
To protect children in vehicles, use age-appropriate car seats and ensure they are installed correctly. Infants and toddlers should be placed in rear-facing seats as long as possible, according to the seat manufacturer’s weight and height limits. Once children outgrow rear-facing seats, transition them to forward-facing car seats with a harness. When they exceed the limits of these seats, use booster seats until seat belts fit properly. All passengers should always wear seat belts, regardless of age. Additionally, avoid distractions while driving, such as using mobile phones, and always adhere to traffic laws to ensure a safe driving environment. In the event that your child is seriously injured in an accident, make sure to consult with an attorney experienced in personal injury law.
By being aware of these common causes of child injuries and implementing effective preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risks and ensure a safer environment for children to grow and thrive. Vigilance and proactive efforts from parents, caregivers, and the community are essential in safeguarding children’s well-being.